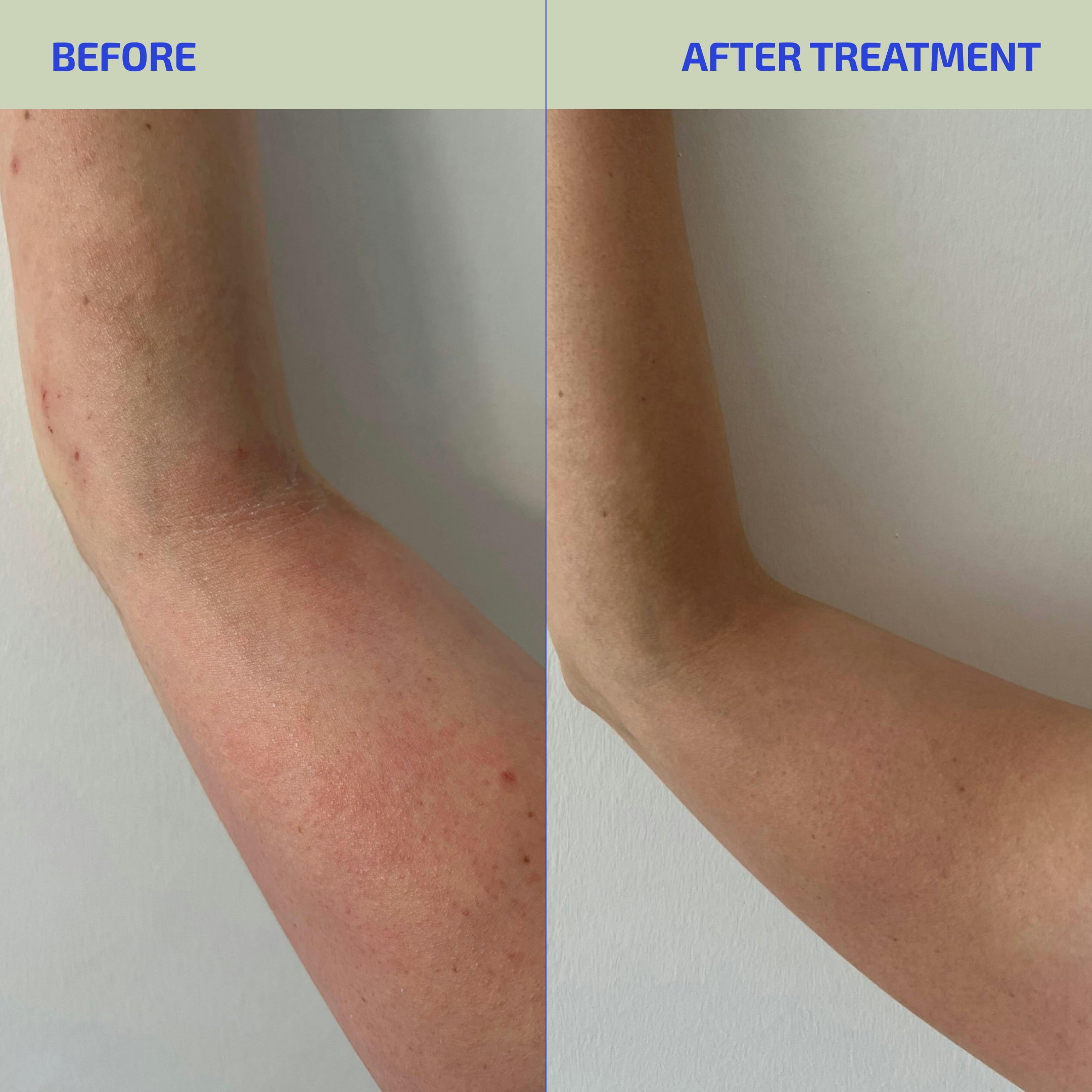
Summary
- Eczema causes red, itchy, inflamed skin due to a compromised skin barrier and immune dysregulation.
- Bath soaks help soothe eczema symptoms by hydrating skin, removing irritants, and restoring skin barrier function.
- Colloidal oatmeal, bleach, salt, baking soda, apple cider vinegar, and magnesium (Epsom) baths are common soak types with specific benefits.
- Each soak works differently-some calm inflammation, others rebalance skin pH or fight bacteria.
- Always moisturize immediately after a soak to lock in hydration and avoid flare-ups.
- Not all soaks work for everyone-patch test and consult a dermatologist for persistent eczema.
Introduction
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is more than just a patch of dry skin-it's a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people, disrupting sleep, self-esteem, and quality of life. Characterized by itchy, red, and irritated skin, eczema flares often feel unmanageable. While prescription creams and moisturizers help, many people overlook one surprisingly soothing remedy: bath soaks.
In addition to being a comforting ritual, bath soaks are also a clinically supported tool for reducing inflammation, removing irritants, restoring hydration, and rebuilding the skin barrier. That said, not all soaks are created equal, and some might even worsen your eczema if used incorrectly. In this article, we'll explore the science behind eczema bath soaks, how they work, and which ingredients to try.

What is Eczema?
Eczema is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory condition whose symptoms include dry, itchy, cracked, or scaly skin. It's typically caused by a combination of factors such as genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers. One hallmark of eczema is a compromised skin barrier, which normally acts like a brick wall to keep moisture in and allergens and microbes out. When the skin barrier breaks down one's skin experiences excessive moisture loss while enabling irritants to penetrate the skin more easily, leading to inflammation and itching.
The condition is most common in children but can persist into adulthood or even appear later in life. People with eczema oftentimes also tend to have a history of other atopic disorders like asthma or hay fever.
Causes of Eczema
Several factors contribute to eczema, including:
- Genetics: Mutations in the filaggrin gene, which helps build the skin barrier, are common in people with eczema.
- Immune Dysfunction: An overactive immune response to normally harmless substances results in chronic inflammation.
- Environmental Triggers: These include soaps, detergents, dust mites, pollen, mold, and harsh climates, both hot and cold.
- Microbiome Imbalance: A healthy (balanced and diverse) skin microbiome helps prevent flare-ups, whereas an unhealthy microbiome tends to have an overgrowth of Staphylococcus aureus, a bacteria linked to eczema severity.
- Stress & Hormones: Psychological stress and hormonal changes can also worsen eczema symptoms.
- Gut Microbiome Imbalance: An imbalance of beneficial and harmful bacteria in the gut (dysbiosis) can disrupt immune regulation. This imbalance may promote heightened allergic responses and inflammation, increasing the risk of eczema.
- Leaky Gut Syndrome: Increased intestinal permeability allows certain proteins and toxins to pass into the bloodstream. This can trigger immune reactions and inflammation that manifest as skin conditions like eczema.
- Food Sensitivities and Allergies: An unhealthy gut microbiome can influence the development of food sensitivities, which may aggravate eczema symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Symptoms and Identification
Eczema can show up as:
- Dry, scaly patches
- Redness and inflammation
- Intense itching (sometimes worse at night)
- Oozing or crusting lesions (in severe cases)
- Thickened skin from chronic scratching
It often appears on the face, neck, hands, inner elbows, and behind the knees. Unlike psoriasis, eczema lesions are not sharply demarcated and tend to be itchier rather than painful.
Treatment Options
Converntional eczema treatments typically include a mix of:
- Topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors: Reduce inflammation and itching, though the use of corticosteroids can lead to topical steroid withdrawal (TSW).
- Skin barrier repair creams: Help to restore and support the skin's lipid layer.
- Antibiotics: For secondary infections.
- Oral medications or biologics: In moderate-to-severe cases.
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding triggers, using humidifiers, and stress management.
Among home remedies, bath soaks are gaining popularity for their ability to reduce symptoms naturally when used as part of a comprehensive regimen.
Why Bath Soaks Help Eczema [1]
Bath soaks improve eczema symptoms by:
- Hydrating and softening dry skin
- Removing allergens, pollutants, and dead skin
- Restoring the skin's pH balance
- Delivering anti-inflammatory or antimicrobial benefits
- Preparing skin to absorb moisturizers more effectively
Think of the skin like a dried-out sponge: if you apply lotion directly to a brittle sponge, it can't absorb it well. But if you moisten it first, it soaks up hydration better. A bath soak primes the skin similarly.
Best Bath Soaks for Eczema [2]
1. Colloidal Oatmeal
- What it is: Finely ground oats suspended in water.
- Benefits: Possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and barrier-protective properties. It contains compounds like avenanthramides that soothe itching.
2. Bleach Baths
- What it is: Diluted sodium hypochlorite (household bleach).
- Benefits: Reduces Staph aureus colonization, decreases inflammation.
- Caution: Use only as directed by a dermatologist.
3. Epsom Salt or Magnesium Baths
- What it is: Magnesium sulfate dissolved in water.
- Benefits: Reduces inflammation, relieves itching, promotes relaxation.
4. Baking Soda
- What it is: Sodium bicarbonate.
- Benefits: Soothes itching and helps rebalance skin pH.
5. Apple Cider Vinegar
- What it is: Acetic acid from fermented apples.
- Benefits: Restores skin's natural acidic pH, mildly antimicrobial.
- Caution: Can sting broken skin, so patch test first.
6. Dead Sea Salt or Mineral Soaks
- What it is: Salts rich in magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
- Benefits: Reduces scaling, inflammation, and itch while enhancing skin hydration.
Important Soak Tips
- Water Temperature: Always use lukewarm water because hot water strips the skin of natural oils and worsens itching.
- Time Limit: Soak for 10-15 minutes. Longer soaks can dry out the skin.
- Moisturize Immediately: Rinse the skin with water then gently pat dry with a towel and apply moisturizer immediately after to seal in moisture/hydration.
- Patch Test: Try new ingredients/products in small areas before a full soak.
- Consult a Dermatologist: Especially if your eczema is infected or severe.
Wet Wrap Therapy [3]
In general, this treatment option involves applying a moist layer of cotton or gauze to an affected area, followed by applying a dry layer, and then keeping it on for a period of time. This method helps hydrate the skin, improve medication absorption, and reduce scratching, especially during eczema flares. Wet wrap therapy is most often used during intense eczema flare-ups or the summer heat when other treatments are not providing sufficient relief.
Flare-up Prevention Strategies [4]
- Establish a gentle daily skincare routine.
- Use fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers.
- Avoid known allergens and irritants.
- Maintain a healthy gut microbiome by consuming pre- and probiotic-rich products.
- Consider antihistamines during flare-ups if prescribed.
Myths and Facts
- Myth: Bleach baths are dangerous.Fact: When used properly, bleach baths are safe and effective against bacterial overgrowth.
- Myth: Only prescription creams work.Fact: Natural approaches like bath soaks can significantly reduce symptoms.
- Myth: Eczema is contagious.Fact: Eczema is neither infectious nor contagious.
FAQ
1. What is the best bath soak for eczema?Colloidal oatmeal and oatmeal in general are widely regarded as the most gentle and effective.
2. Are bleach baths safe for kids with eczema?Yes, when used under pediatric supervision and in the right dilution.
3. How often should I take eczema soaks?2-3 times per week is generally safe, but frequency should be based on skin tolerance.
4. Can apple cider vinegar worsen eczema?Yes, if applied to open or sensitive skin. Always dilute and patch test.
5. Do Epsom salt baths help eczema?They can reduce inflammation and soothe the skin, especially during stress-related flares.
6. Should I rinse after a bleach bath?Yes, a quick rinse in clean water is recommended, followed by moisturizing.
7. Is a magnesium soak or wrap good for eczema?Yes, magnesium can help calm skin and reduce itching.
8. Are essential oils safe in bath soaks?Generally not for eczema. They can irritate sensitive skin unless specifically designed for eczema-prone users.
9. Can I use bubble bath if I have eczema?No, most bubble baths contain surfactants and fragrances that worsen eczema.
10. Is daily bathing bad for eczema?Not if done with lukewarm water, gentle cleansers, and immediate moisturization.
11. What is the main difference in benefits between a bleach bath and a salt wrap?
- For infection control and flare reduction, bleach baths are often recommended by dermatologists.
- For soothing, hydration, and itch relief, salt wraps can be beneficial.
- In many cases a combination of both can help manage flares
Conclusion
Bath soaks and wraps can be a soothing and scientifically backed addition to your eczema care routine. From oatmeal to Dead Sea salt, each soak offers unique benefits to relieve itching, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. The key lies in choosing the right soak for your skin, using it correctly, and always following up with skin barrier-repairing moisturizers and supplements.
Call to Action
At Codex Labs, we take treatment and management of chronic inflammatory skin conditions like eczema VERY seriously. So seriously, in fact, that we tackle the problem from both inside and outside the body. To help manage your eczema-related symptoms from inside the body, you owe it to yourself to try our clinically proven ANTU SKIN BARRIER SUPPORT SUPPLEMENT containing the amino-acid l-histidine together with our potent antioxidant workhorse M3+. Taken daily, this delicious tasting cocktail will help to provide much needed eczema symptom relief from within your body by helping it build filaggrin protein that fortifies your skin barrier and reduces de-hydration.
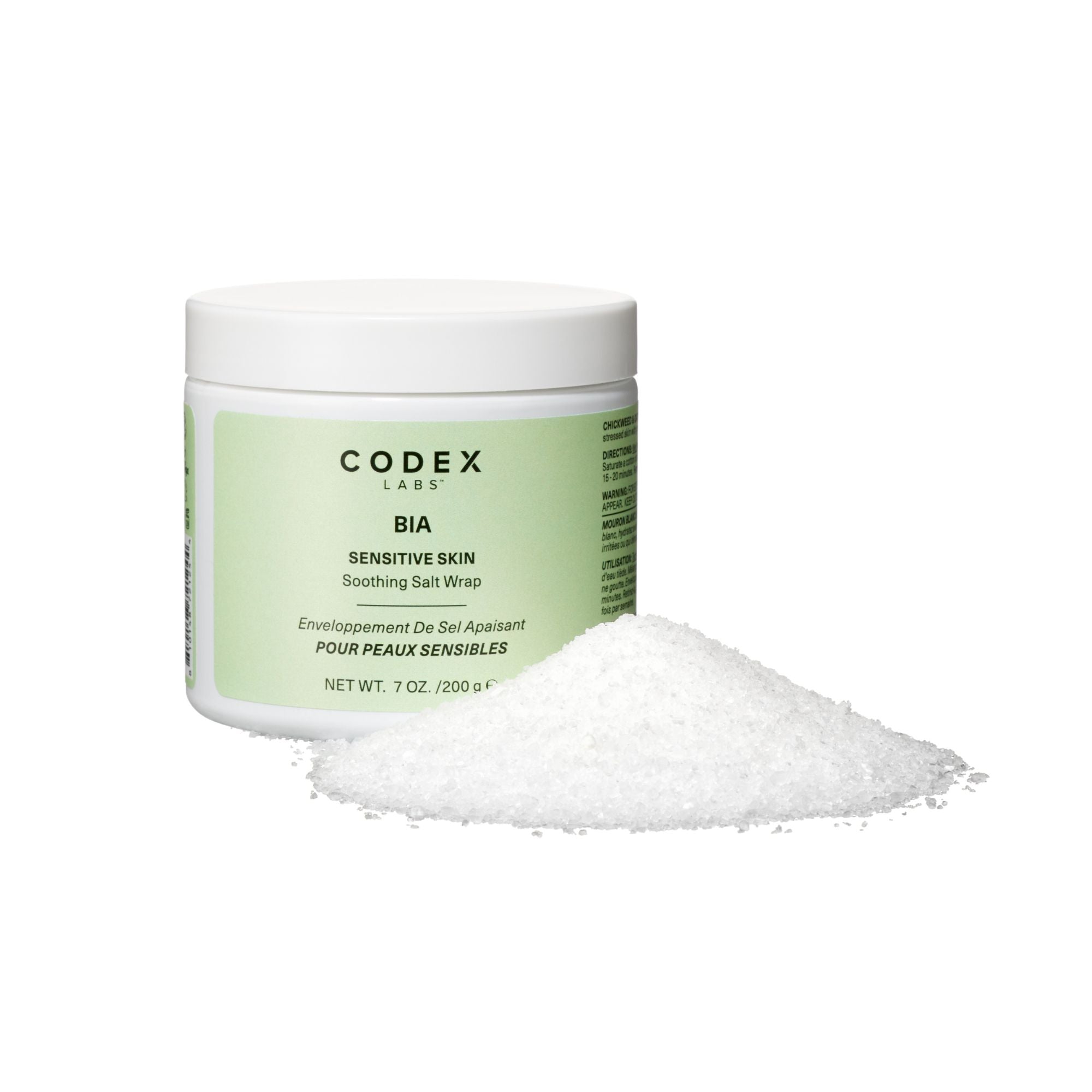
And for those times when your itch symptoms are especially intense feeling, you really should try our newly launched BIA SENSITIVE SKIN SOOTHING SALT WRAP for use outside the body as a soothing wrap. Salt wraps leverage the natural anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and skin-healing properties of salt to help reduce irritation (cleanse skin by drawing out toxins), create a mildly antimicrobial environment (prevent infections), improve skin hydration, and ultimately help repair a compromised skin barrier. Our microbiome-supporting, soothing salt wrap combines Epsom and Sea salts having a full range of minerals (magnesium, calcium, and potassium) with tapioca starch to slowly release comforting plant-extracts to help manage intense discomfort like itching or burning, as well as emollient oils for skin moisturization, and repair. So, the next time you experience an eczema flare that requires some added attention, do yourself and skin a favor and apply a salt wrap to the problem area. It will definitely turn your uncomfortable frown upside down!
Reviews
Eczema Neutralized *****
- Ashley Miles
I had pretty bad eczema flair the day this was delivered. I soaked and got more relief than other oatmeal baths I've tried. Definitely keeping this on hand.
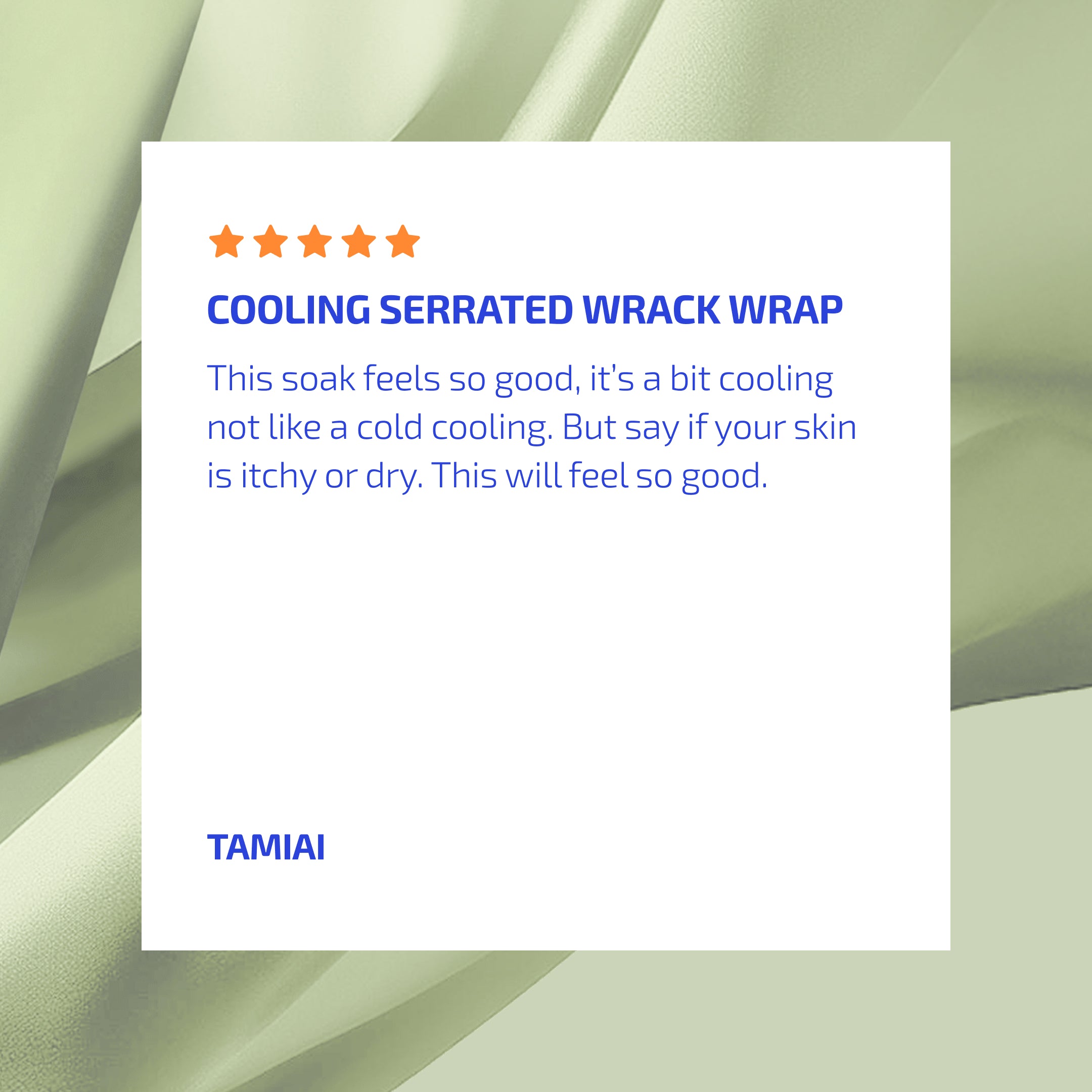
Cooling Serrated Wrack Wrap *****
- Tamiai
This soak feels so good, it's a bit cooling not like a cold cooling. But say if your skin is itchy or dry. This will feel so good.
Soothing & Calming *****
- Carlyssa W.
We all love a good relaxing and self-care moment. With Codex labs sea salt soak you are able to take care of your skin and yourself. I have very sensitive skin and I didn't find any irritation with this product.
References
2. https://nationaleczema.org/treatments/bathing/
3. https://nationaleczema.org/blog/colloidal-oatmeal-bath/
4. https://nationaleczema.org/treatments/wet-wrap-therapy/
5. https://eczema.org/information-and-advice/living-with-eczema/flare-ups/