Key Takeaways
- Glutamine is a key fuel and building block for the cells that line your intestines, making it central to gut lining support and defense.
- Research suggests glutamine can help maintain tight junctions, reduce intestinal permeability, and support “leaky gut repair” in specific stress or illness settings—though it’s not a magic cure-all.
- The benefits of glutamine extend beyond digestion: it also supports immune balance, mucous production, and a healthy relationship between your gut microbes and gut barrier.
- Glutamine for gut health works best as part of a broader plan: nutrient-dense diet, stress management, sleep, and targeted medical care where needed.
- Supplementation can be helpful for some (e.g., athletes under intense stress, hospitalized or critically ill patients under supervision), but dosing, timing, and safety should always be personalized with a healthcare professional.

Why Your Gut Barrier Needs a Bodyguard
Imagine your gut as a long, high-security border crossing. On one side: food, microbes, toxins, and chemical signals. On the other: your bloodstream, organs, and immune system.
Separating the two is a one-cell-thick wall, the intestinal lining, held together by tiny “gates” called tight junctions. When this wall is healthy and functioning as it should, your body absorbs nutrients efficiently while keeping troublemakers (ex. toxins) out. When it’s compromised, unwanted bad actors can sneak through, potentially driving inflammation and symptoms many people metaphorically describe as “leaky gut.”
Enter glutamine, the most abundant amino acid in the body and a preferred fuel source for the cells that make up your intestinal lining. It plays a crucial role in gut lining support, immune balance, and repair processes that protect your gut barrier. In this article, we’ll break down the science of glutamine and gut health in clear terms: how glutamine supports the gut barrier, where the evidence is strong, where hype outruns the data, and how to think about glutamine supplementation as part of a smart, science-backed approach to glutamine and intestinal health.
What Is Glutamine and What Is the Gut Barrier? [1]
Glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid. Under normal conditions, your body can make enough. However, when the body experiences stress, intense exercise, infection, trauma, surgery, or chronic illness, glutamine demand can outpace supply.
The gut barrier is made up of several layers:
- Gut Microbiome – the beneficial microbes that help digest food and educate your immune system.
- Mucus layer – a gel-like coating that keeps most bacteria at arm’s length from the gut wall.
- Epithelial cells – a single-cell layer forming the physical wall.
- Tight junctions – protein “zippers” between cells that decide what gets through.
- Immune cells underneath – ready to respond to true threats.
Glutamine and gut health are tightly linked because intestinal cells (enterocytes) use glutamine as one of their primary energy sources, especially for growth, repair, and maintaining tight junctions.
What Damages the Gut Barrier? [2]
There are numerous factors that can weaken this barrier including:
- Highly processed, low-fiber diets
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Certain medications (ex. NSAIDs), when used frequently
- Severe or chronic stress
- Infections or inflammatory bowel disease
- Intense, prolonged exercise in the heat
- Severe illness, burns, or major surgery
When these factors manifest, tight junctions in the wall can become loose, a phenomenon known scientifically as increased intestinal permeability, a.k.a., “leaky gut.” While “leaky gut syndrome” as a catch-all diagnosis is still debated, the underlying biology, i.e., barrier damage and increased permeability, is very real and measurable.
Here’s where glutamine supplementation for gut health becomes relevant. In many experimental models, glutamine helps restore tight junction proteins, reduces permeability, and supports mucosal healing.
How Might You Notice a Compromised Barrier?
No at-home gadget can definitively tell you that you have a “glutamine deficiency” in your gut or a clinically validated “leaky gut.” That said, certain experiential patterns may suggest barrier stress, such as:
- Bloating, gas, or discomfort after meals
- Loose stools or urgency
- Symptoms flaring with consumption of alcohol, ultra-processed foods, or NSAIDs
- Co-existing inflammatory or immune issues (IBD, some autoimmune conditions), where barrier dysfunction is part of the picture
Analogy: if your gut barrier is a coffee filter, barrier dysfunction is like tiny tears that let grounds into your cup wherein more mess equals more irritation. Glutamine’s role is to help repair the filter material, not just skim the grounds off the top.
How Glutamine Supports the Gut Lining [3]
1. Fuel for Gut Cells
Enterocytes burn glutamine for energy more readily than they burn glucose. When glutamine is available, these cells:
- Turn over efficiently (old, damaged cells are replaced quickly)
- Maintain normal structure of gut villi and crypts
- Are better equipped to recover from physical, chemical, or inflammatory stress
2. Tight Junction & Barrier Integrity
Glutamine has been shown to:
- Upregulate tight junction proteins (like occludin and claudins)
- Reduce cytokine-induced disruption of these junctions
- Help normalize permeability in certain models of injury or stress
In human and animal studies:
- Supplementation has been shown to reduce markers of intestinal permeability in athletes experiencing stress due to extreme exercise, as well as in some hospitalized patients.
- A 2024 meta-analysis reported that, in specific short-term, higher-dose protocols, glutamine supplementation improved measured intestinal permeability.
3. Immune and Microbiome Support
Glutamine feeds rapidly dividing immune cells and may help:
- Modulate excessive inflammation
- Support a gut microbiome environment that favors barrier-protective species over those that promote inflammation and permeability
Practical Ways to Use Glutamine for Gut Lining Support
If you’re considering glutamine for gut health or leaky gut repair as part of a comprehensive plan, here’s a simple framework (to be individualized with your provider):
Step 1: Start With Food
You naturally get glutamine from:
- Meat, poultry, fish
- Eggs
- Dairy (if tolerated)
- Beans, lentils
- Cabbage, spinach, beets
For many, a protein-sufficient, whole-food diet covers baseline needs for glutamine and intestinal health.
Step 2: Consider Supplemental L-Glutamine (With Guidance)
Common user-style approaches (not personal medical advice):
- Typical oral doses often fall around 5–15 g/day.
- Used 30–60 minutes before meals or between meals for targeted gut lining support.
- Look for pure L-glutamine powders without unnecessary sweeteners or irritants.
Who can benefit from discussing glutamine supplementation with a clinician?
- Endurance athletes with gut issues during heavy training
- Individuals with medically recognized states of increased permeability or gut injury (IBD, short bowel, critical illness) under supervision
- People on gut-healing protocols overseen by a gastroenterologist, registered dietitian, or knowledgeable clinician
- Those with symptoms indicating a potential leaky gut disorder
Who should be especially cautious or avoid supplementation:
- Those with significant liver or kidney disease
- Those with certain metabolic disorders
- Anyone on complex medication regimens, chemotherapy, or with a history of severe medical issues must first clear it with their medical team
Myths vs. Facts
Myth 1: “Glutamine alone cures leaky gut in everyone.”
Fact: Glutamine can support the gut barrier and may improve permeability in some contexts, but diet, stress, sleep, current microbiome mix, and underlying disease all matter.
Myth 2: “If you’re bloated, you’re deficient in glutamine.”
Fact: Bloating has many causes; there’s no simple at-home test that says “you need glutamine.”
Myth 3: “More is better.”
Fact: Very high doses aren’t automatically more effective and may not be appropriate for everyone. Targeted, supervised use is smarter.
Myth 4: “Glutamine is unsafe.”
Fact: For many healthy adults, short-term use at common doses appears to be very well tolerated, but medical context matters.
How to Choose a Glutamine Product for Gut Support
When evaluating a glutamine gut barrier or leaky gut repair product, look for:
- Pure L-glutamine (no proprietary blends hiding low doses)
- Transparent dosing (grams per serving clearly listed)
- Minimal additives: avoid unnecessary dyes, artificial sweeteners, or known GI irritants
- Third-party testing or quality certifications
Pair any glutamine supplement with:
- A high-fiber, plant-rich diet
- Omega-3s and polyphenol-rich foods
- Stress management, movement, and sleep represent non-negotiable co-therapies for gut lining support
FAQ
1. What are the benefits of glutamine for gut health?
Glutamine helps fuel intestinal cells, support tight junctions, modulate immunity, and may reduce intestinal permeability in certain settings—key aspects of glutamine and gut health.
2. How does glutamine support the gut barrier?
It acts as energy and raw material for gut cells, supports mucous production, and helps maintain tight junction proteins—central to a strong glutamine gut barrier.
3. Can glutamine help with leaky gut repair?
It may contribute to leaky gut repair by improving barrier integrity, especially under stress, but should be combined with medical evaluation, diet, and lifestyle changes.
4. Is glutamine good for overall gut lining support?
Yes. Glutamine is one of the main amino acids used by intestinal cells, making it a logical tool for gut lining support when used appropriately.
5. How much glutamine should I take for gut health?
Many protocols recommend consuming about 5–15 g/day. Check with your physician for the dose most appropriate for you.
6. How fast does glutamine work for gut issues?
Some studies show changes in permeability within days to weeks, but symptom relief varies. It’s not an instant fix.
7. Can I get enough glutamine from food instead of supplements?
Typically, yes with adequate protein intake from whole foods. Supplements are considered when needs are higher or intake is limited.
8. Is glutamine safe for long-term use?
Short-term or low dose (1-2 g/day) use appears safe for many, but long-term, high-dose use should be supervised, especially if you have medical conditions.
9. Can glutamine help both gut and immune health?
Yes. Supporting the gut barrier with glutamine and intestinal health benefits can indirectly support immune balance, as much of the immune system lives in the gut.
10. Who should not use glutamine for gut health without supervision?
People with liver or kidney disease, serious medical conditions, cancer, or on complex medications should only use glutamine under professional guidance. Glutamine supplementation in kids is still under evaluation by the medical community.
Conclusion
Glutamine sits at a fascinating crossroads of nutrition, gut biology, and immune health. Used wisely, it can:
- Support the structure and function of your gut barrier
- Complement broader strategies for gut lining support
- Offer targeted benefits in specific, stress-heavy or medically supervised contexts
It is not a substitute for a solid diet, appropriate medical evaluation, or evidence-based management of underlying conditions. But as part of a comprehensive plan, the benefits of glutamine for gut health are scientifically plausible, increasingly supported in defined settings, and worth an informed conversation with your healthcare team.
Call to Action
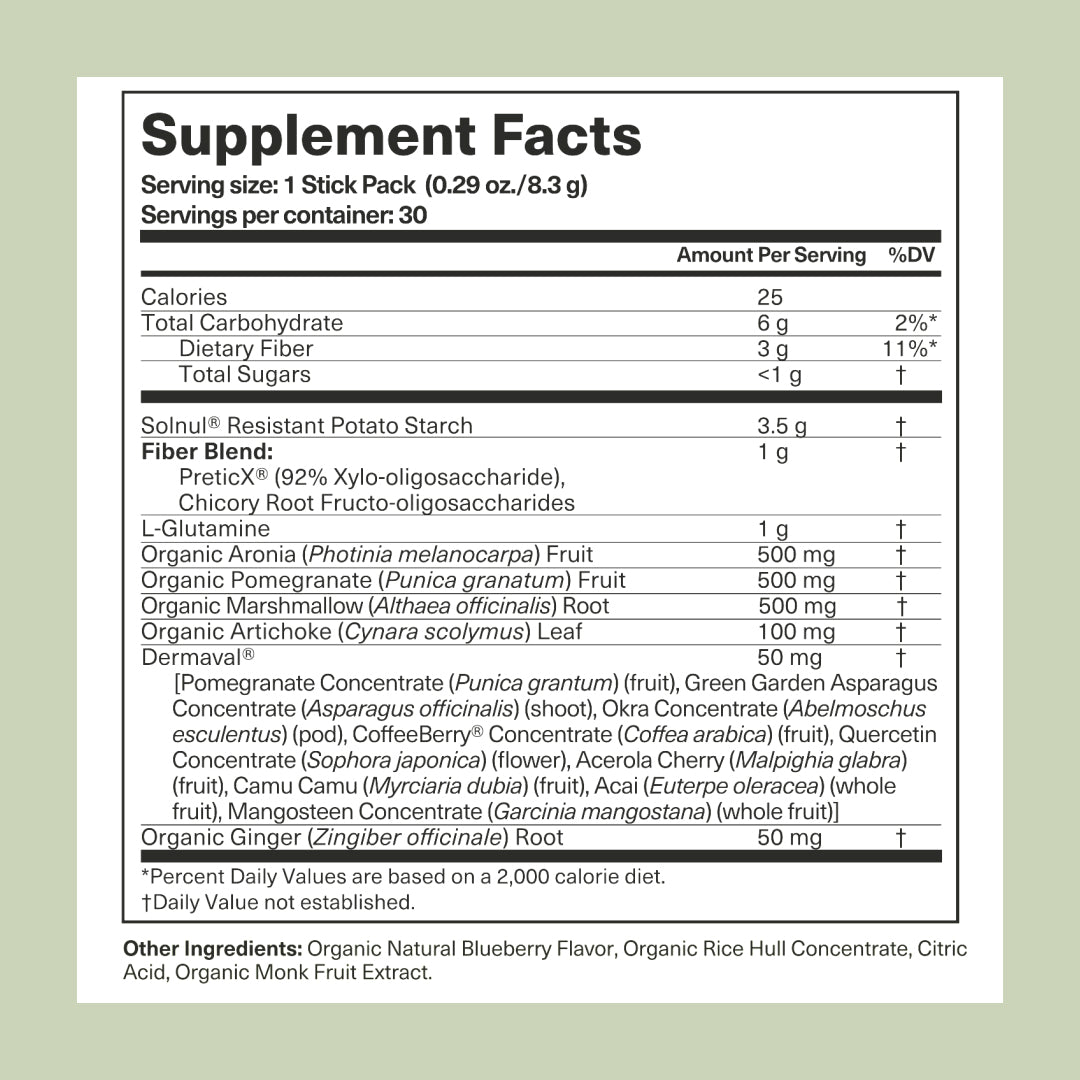
At Codex Labs, we researched and vetted numerous plant-based and biologically derived actives to develop a scientifically backed, patent-pending supplement formulation specifically directed to enhancing and maintaining gut health/integrity and microbiome balance/diversity. Our BIA GUTBUILDER PREBIOTIC SUPPLEMENT, with key actives like resistant potato starch, chicory root, marshmallow root, aronia berry pumice, and of course, L-glutamine, coupled with key superfoods targeting gut inflammation and motility, is a power packed foundational prebiotic supplement that provides the gut with the fuel it needs for optimized functionality/diversity while keeping intestinal wall junctions tightly packed.
And for those individuals who regularly struggle with unexpected acne flare-ups, we have our patented SHAANT CLEAR SKIN PROBIOTIC SUPPLEMENT which, when combined with the BIA GUTBUILDER PREBIOTIC SUPPLEMENT, provide your gut microbiome with the ideal intestinal environment for establishing a healthy, balanced, well diversified gut microbiome that will help you manage acne flare-ups from inside your body.
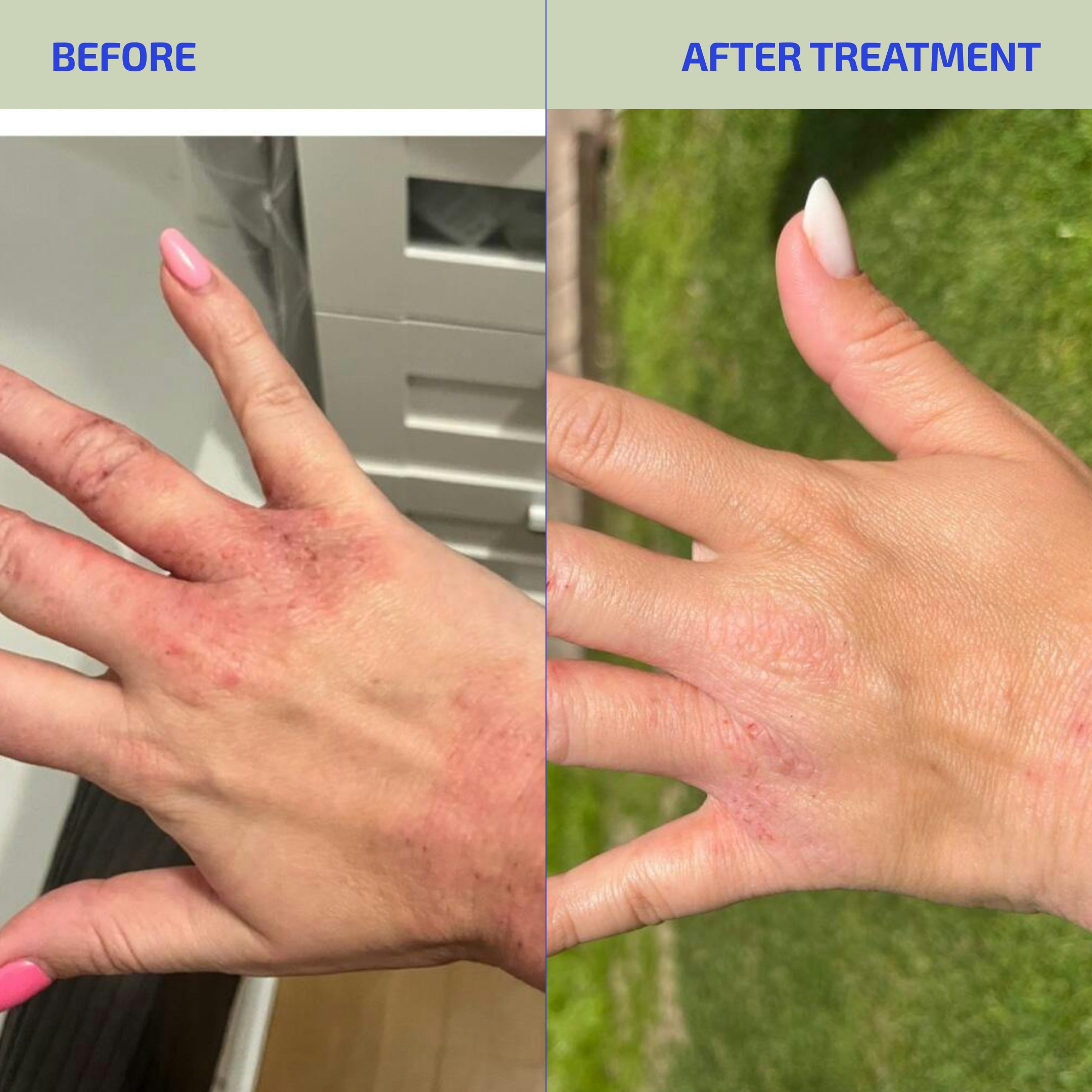
Similarly, for those individuals trying to manage and minimize eczema flare-ups, we have our patent-pending BIA CLEARSKIN SYNBIOTIC SUPPLEMENT which combines bacterial species from three key genera with a prebiotic having antioxidant properties (blueberry powder) to help restore gut microbiome balance, improve gut immunity, reduce inflammation, all while increasing skin ceramide production..Your skin will reward your efforts by looking as good as it feels. How can we be so sure? Because we have the clinical data to prove it!
References:
1. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27749689/
2. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S246812532400390X
3. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4369670/